Slow-healing wounds are a challenge for both patients and doctors, as they interfere with daily life and can lead to more serious health problems in the long run. Why do wounds heal slowly? Proper nutrition, stress management, regular sleep and physical activity are important factors in maintaining good health immune system and reducing inflammation, which is one of the main factors inhibiting wound healing. In this article, we'll discuss how to recognize slow-healing wounds and provide tips on how to prevent them, including vital nutrients to promote faster healing.1
In examining the causes of slow healing, we will look at the effects of nutrition, important nutrients such as zinc, vitamin D and vitamin E, and how physical activity and adequate rest contribute to a healthier wound healing process. We will provide practical tips and prevention strategies for those facing slow healing challenges, including a non-healing leg wound, and how to effectively use these techniques to speed up the healing process.
How to recognize slow-healing wounds
Determining whether or not slow-healing wounds are true can be difficult, but there are some clear signs to watch for. One of the main indicators is the duration of wound healing, which depends on various factors:
- The size of the infected area: Large lesions usually require more time to heal.
- Type of infection: Different pathogens can cause different healing rates.
- Is the wound bleeding?: Bleeding can interfere with normal wound healing.
- The presence of pus: Pus indicates an inflammatory process that can delay healing.
- Personal health status: General health and immune function are important factors in the healing process.
Observing these signs can help you better understand when a wound is healing slowly and when additional medical attention is needed.

Interesting facts about wound healing
Macrophages are important cells of the immune system that play an essential role in fighting infections. They not only consume foreign bodies, but also promote wound healing. A proper diet with enough protein, vitamins A and C, and zinc can significantly speed up the healing process. In addition, light physical activity improves blood circulation, but vigorous exercise should be avoided until the wound has healed.
Myths and facts about wound healing
- Myths: Wounds heal faster if we keep them open.
- The facts: Wounds should be kept free from dirt and bacteria to prevent infection and ensure faster healing.
- Myths: All wounds heal equally.
- The facts: There are different types of wounds, including surgical, traumatic, and slow-healing wounds, each with unique healing processes.
- Myths: Antibiotic ointment prevents scarring.
- The facts: Although antibiotic ointment can help prevent infection, it does not affect scarring.
Important tips for wound care
- It is recommended to use cold compresses on the first day of the injury to reduce swelling, and warm compresses afterwards.
- Povidone-iodine (Betadine) solution is an effective antiseptic against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, fungi, spores and some types of viruses.
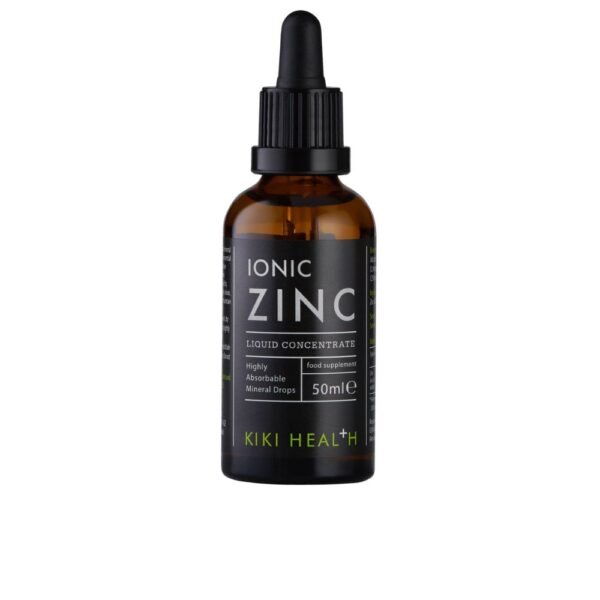
- Zinc supplements can strengthen the immune system and reduce the severity of infections, and vitamin D is essential for a healthy immune system and helps regulate the immune response.
-
Sale Product on saleKIKI Health ionic Zinc, liquid concentrate, 50ml
29,90 €Original price was: 29,90 €.25,40 €Current price is: 25,40 €.Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 2 customer ratings
Causes of slow healing wounds
Slow-healing wounds can occur for a variety of reasons, which include both medical conditions and everyday habits. Here are some of the main factors that affect wound healing:
- Diabetes and its effects: Diabetes is one of the most well-known causes of slow-healing wounds, especially in the leg area. This disease can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to reduced sensation in the legs and an increased risk of injury.
- Improper footwear and foot care: Footwear that does not fit or is not suitable for the activity can cause injuries. In addition, insufficient foot care, such as improperly trimming nails or ignoring minor injuries, can also cause problems.
- Physical activity and injuries: Regular participation in outdoor activities such as running or cycling can increase the risk of injury, especially if the activity is performed improperly or unsafely.
- Age and a slower metabolism: Older people are at greater risk due to reduced flexibility, balance and strength. In addition, a slower metabolism can make healing more difficult and reduce the tolerance of certain medications.
- Psychological factors: Stress and sleep disturbances can negatively affect the immune system and the wound healing process. Research shows that high work stress can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, which in turn can slow wound healing.
These factors reveal that the causes of slow-healing wounds are complex and multifaceted, requiring individual attention and preventive measures to ensure faster and more effective healing.
Effect of nutrition on wound healing
A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is vital for wound healing. Vitamins A and C and zinc are the main nutritional components that help speed up regeneration processes. Zinc is especially important, because it is involved in the production of collagen, which is an essential component of wound healing, and reduces the risk of infection.
Food sources
- Seafood: Rich source of zinc.
- Meat: Red meat in particular contains zinc.
- Nuts and seeds: A great way to get the zinc you need.
- Beans: Legumes like beans are also a good source of zinc.
- Dairy products: Provides the body with zinc and essential fatty acids.
- Eggs and whole grain products: Additional sources of zinc.
Importance for the Immune System
Zinc, vitamin D and E are essential for boosting the immune system, especially when fighting infections that can arise from wounds. These nutritional components help activate macrophages, which are important cells of the immune system responsible for regulating the inflammatory response and healing damaged tissue.
Diet and Health
A balanced diet rich in protein and nutrients is essential not only for wound healing but also for general health. Eating a regular and balanced diet helps prevent weight gain, which can put extra pressure on wounds and slow their healing. Controlling portion sizes and avoiding high-calorie, low-nutrient foods can help maintain a healthy weight and promote faster wound healing.

Wounds that heal slowly are related to physical activity and rest
Regular physical activity and adequate rest are integral to health and a well-functioning immune system. This is especially important for the wound healing process, which requires the body's ability to effectively fight infections and promote tissue regeneration.
Regular exercise and its effects
- Easy exercises, such as yoga or jumping, stimulates the activity of the lymphatic system and improves blood circulation, which is necessary for faster wound healing.
- Deep breathing exercises and incorporating relaxation techniques, such as meditation or progressive muscle relaxation, into your daily routine helps support lymphatic function.
- Physical therapy, including ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or laser therapy, can be used to stimulate blood flow, reduce swelling, and promote tissue growth.
The importance of rest
Adequate rest and sleep are vital for the immune system. Quality sleep helps restore the body's strength and fight infections more effectively, which is necessary to ensure smooth healing of wounds.
Physical therapy methods
- Ultrasound therapy: Uses sound waves to help increase blood flow and promote tissue growth.
- Electrostimulation: Stimulates tissue growth and relieves pain, used to treat venous and arterial ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers.
- Laser therapy: Uses light energy to stimulate tissue growth and reduce inflammation and is used to treat diabetic feet, venous ulcers and pressure ulcers.
These methods are important not only for wound healing, but also for overall body health, helping to maintain optimal weight and improving psychological well-being.

The most important nutrients that accelerate wound healing
Zinc supplements are integral to a strong immune system and can reduce the severity of infections. Vitamin D is essential for a healthy immune system and helps regulate the immune response, while vitamin E has antioxidant properties that protect cells from damage. Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin E are essential to stimulate macrophages and strengthen the immune system.
Basic nutrients
- Zinc: Stimulates the production of collagen, an important component of wound healing.
- Vitamin D: Regulates the immune response, helps fight infections.
- Vitamin E: Protects cells from oxidative stress, promotes cell renewal.
These nutrients are vital not only for wound healing but also for overall immune system support.
Medical treatment for slow-healing wounds
Effective antiseptics and their use
- Povidone iodine (Betadine): Effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, fungi, spores and some viruses. 10% solution kills bacteria in 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate: Used as disinfectants to help clean wounds and reduce the risk of infection.
Innovative technologies for wound treatment
- The work of KTU scientists: A three-part device for the management of diabetic foot syndrome includes a dermatoscopy camera, a light filter system, and a thermographic camera. This device helps determine the size and depth of ulcers and detect inflammation or infection.
- Software: Compares the temperatures of both feet and alerts healthcare professionals to significant differences that may indicate an infection or ulcer.
Modern materials and their application
- New structures with antimicrobial properties: Developed by KTU scientists, these materials mimic the natural extracellular matrix, promoting tissue regeneration. The main component is hyaluronic acid, which is widely used in medicine to stimulate tissue regeneration.
An integrated approach to treatment
- Hydrocolloid dressings and alginate dressings: Effectively absorbs exudate, reduces leakage, promotes angiogenesis and prevents bacterial invasion. Alginates, due to their strong hydrophilic properties, quickly absorb the secretion, and the fiber absorbing the wound secretion turns into a gel mass that safely covers the wound.
- Granulox gel: Hemoglobin-based gel for topical care of dry and wet wounds, controls wound microclimate and promotes healing.

Prevention and care tips
General health care tips
- Protect yourself from scratches and bruises: During the summer, it is important to be careful when participating in various activities to avoid accidental injuries.
- Protect your eyes and cover your skin during allergy season: This will help reduce the risk of allergic reactions and inflammation.
- Consult a specialist if the wound does not heal for a long time: It is important to get professional medical help in time to prevent more serious health problems.
Important tips for infection prevention
- Be alert for symptoms of common summer illnesses: Early recognition of symptoms can help to start treatment sooner and avoid complications.
- Consult a doctor if the wound persists, emits an unusual odor, or the surrounding skin is red and swollen: These signs may signal more serious infections.
- Use disinfectants: This will help prevent the spread of viruses and bacteria, especially in public places and when in contact with other people.
Strengthening the immune system
The immune system has three main functions: it fights pathogens, removes infected cells, and helps you recover faster from illness. In order to ensure its effective operation, it is necessary:
- Balanced diet: Make sure your diet is rich in all essential vitamins and minerals.
- Regular physical activity: It helps in maintaining a strong immune system.
- Sufficient rest and sleep: Sleep is vital for restoring immune function.

FAQ Part: Slow Wound Healing
What causes slow wound healing?
Slow wound healing can occur for a variety of reasons, including poor circulation, inflammatory conditions, diabetes, malnutrition, and infections. Also, smoking and taking certain medications can negatively affect wound healing.
How can wound healing be accelerated?
An effective way to speed up wound healing is to ensure adequate nutrition, avoid smoking, and follow your doctor's instructions for wound care. It is also important to regularly check the condition of the wound and, if necessary, consult a health care professional.
What are the symptoms of a slow wound healing?
If the wound does not start to improve or gets worse after several weeks, this may be a sign of slow wound healing. Other symptoms include increased pain, pus, redness, or warmth around the wound.
When to see a doctor about slow wound healing?
If you notice that the wound not only does not heal, but also new symptoms appear, such as heat, severe pain or a strange discharge smell, see a doctor immediately. This is especially important for individuals with chronic illnesses.
Conclusions
Slow wound healing is a complex process that is affected by many factors, including the individual's health status, lifestyle, and timely and appropriate treatment. Effective wound healing is critical to health, so it is extremely important to be vigilant and follow the information outlined above.
Understanding and responding appropriately to slow wound healing can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent more serious complications. Health care professionals can offer a variety of strategies and treatments to help promote faster and safer wound healing.












One comment
Martin G.
Loved the tips. Now I know why I have this problem. Thanks for the extras