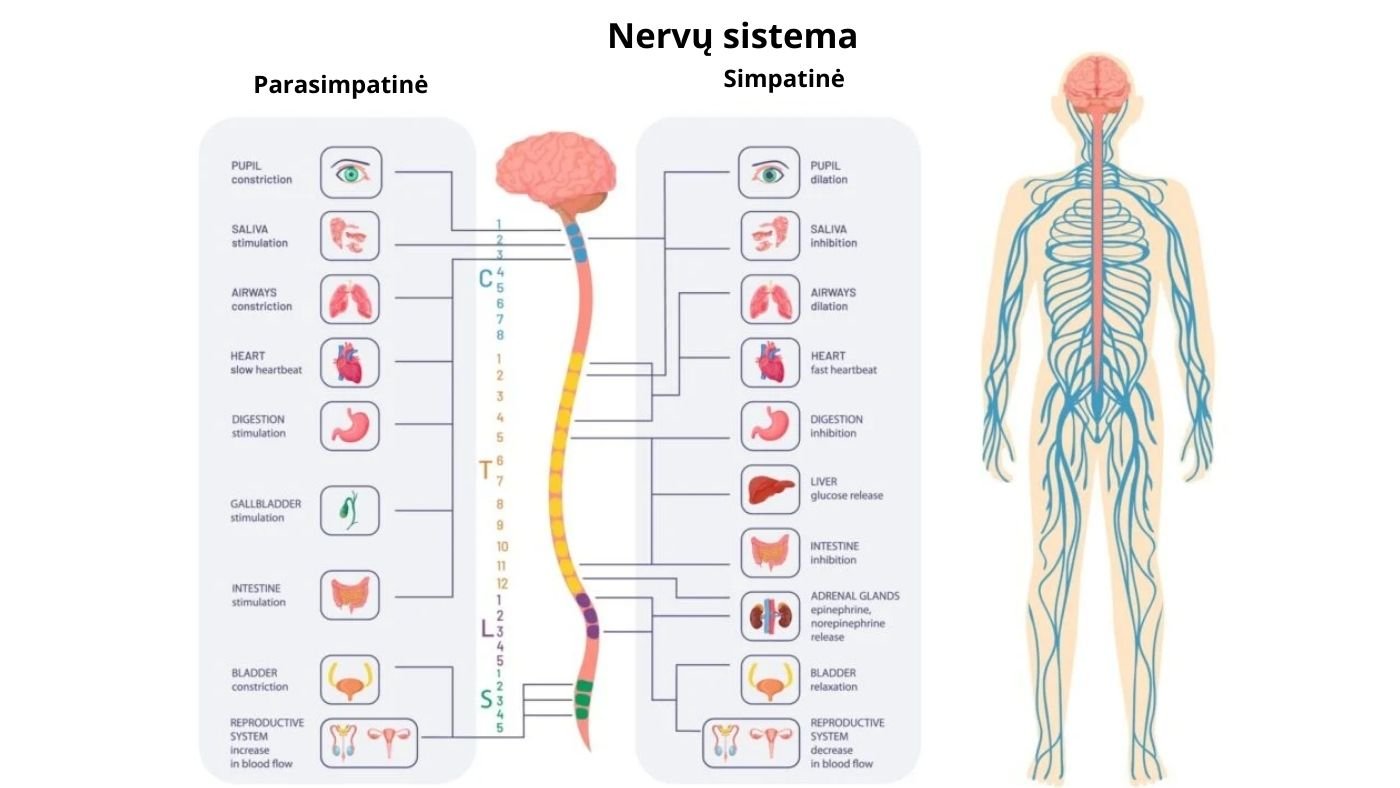
The sympathetic nervous system is a part of our body whose influence is often underestimated. It is a complex biological mechanism that works without our conscious control, but its activity is crucial for our daily well-being and health. In this article, we will take a detailed look at how the sympathetic nervous system works and explain why its healthy functioning is vital.1
The sympathetic nervous system is the part of the autonomic nervous system that regulates the functioning of our internal organs. It is responsible for the body's response to stress and threats, and also regulates body functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, sweating, etc.
Introduction to the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is part of the autonomic nervous system, often referred to as the "fight or flight" system. It is responsible for the body's reaction to stressful situations, mobilizing the energy and resources needed for a quick response. The SNS operates without our conscious control, responding to external and internal signals to ensure the functioning of vital organs and adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
The sympathetic nervous system consists of nerve fibers that originate in the midbrain and spinal cord. Its purpose is the transmission of signals from the central nervous system to various body organs. These signaling circuits are vital because they regulate many involuntary physiological processes, such as heart rate, respiration, digestion, and metabolism.
Since the SNS is responsible for preparing the body for stressful situations, it is also involved in the release of hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline. These hormones increase the activity of the heart, blood pressure, pulmonary air flow and the proper distribution of energy resources in the body.

Understanding the functions of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system acts as an orchestra that harmonizes the functioning of various body systems. One of the most important functions of the SNS is to maintain homeostasis, or the internal balance of the body's environment. This includes temperature regulation, pH balance and electrolytes maintaining levels that are necessary for the normal functioning of cells, tissues and organs.
The SNS also regulates the cardiovascular system. It increases heart rate and strength to increase blood flow to muscles and other important organs. In addition, the sympathetic nervous system controls the constriction or dilation of blood vessels, thereby regulating blood pressure and ensuring optimal blood circulation.
The activity of the digestive system is also controlled by the SNS. During times of stress, the sympathetic nervous system slows down gastrointestinal motility and food digestion, allowing the body to focus on more immediate tasks. This adaptive function is very important because it allows the body to allocate energy resources efficiently.
How the sympathetic nervous system works
The sympathetic nervous system operates through a complex network of nerve impulse transmission. When our brain perceives a threat or stress, the sympathetic nervous system kicks in and starts a chain of signal transmission. This circuit begins in the brain, which transmits signals to the spinal cord and from there to the sympathetic ganglia. Ganglia are groups of nerve cells that are responsible for transmitting signals to specific organs.
When sympathetic nerve fibers reach their target organs, they release noradrenaline and other chemical mediators that bind to specific receptors on the cell surface. This causes changes in cellular activity, which is the result of the action of the sympathetic nervous system. For example, when heart cells bind to noradrenaline, they begin to contract faster and harder.
In addition to these direct nerve fiber effects, the sympathetic nervous system also acts through the endocrine system. It stimulates the release of hormones from the adrenal cortex, such as adrenaline, into the blood. These hormones act as signals that reach all corners of the body, thus further amplifying the effects of the SNS.
The role of the sympathetic nervous system in our health
The activity of the sympathetic nervous system is an integral part of our daily functioning. It ensures that our body can respond quickly and efficiently to challenges when needed. Without SNS, we would be much less adaptable to sudden changes in our environment and more susceptible to injury or even death.
The SNS is also important in fighting infection and inflammation. It affects components of the immune system, such as white blood cells, and makes them more active. Also, the sympathetic nervous system regulates body temperature, helping to maintain optimal conditions for the activity of all types of cells.
However, SNS activity must be balanced. Over-activating it over a long period of time can lead to chronic stress, which is linked to many health problems such as high blood pressure, heart disease, obesity and diabetes. Therefore, it is important to find a balance between the functioning of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems so that our body can function optimally.
Effects of disorders of the sympathetic nervous system on health
There are many different conditions that can affect the sympathetic nervous system. For example, prolonged stress or anxiety can weaken the sympathetic nervous system, which can increase the risk of obesity and other metabolic problems. In addition, certain genetic conditions, trauma, infections, or long-term drug and alcohol use can cause long-term nerve damage and disorders of the sympathetic nervous system.
Disorders related to the activity of the sympathetic nervous system can have various negative effects on our health. For example, hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system can cause phenomena such as high blood pressure, heart rhythm disorders and other cardiovascular problems. Meanwhile, too little SNS activity can cause a lack of energy, a reduced response to stress, and even immune system dysfunction.
One of the most common SNS-related disorders is a syndrome called "autonomic dysfunction" or "autonomic neuropathy." It is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which includes the SNS, does not function properly. This can cause a number of symptoms such as digestive problems, loss of bladder control, weight loss or increased sweating.

Ways to improve the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system
Practicing healthy habits and lifestyle is important to ensure a healthy functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This includes regular physical activity, which helps regulate SNS activity, reducing levels of stress hormones and stimulating the production of endorphins, the so-called "happy hormones."
Meditation and breathing exercises can also effectively reduce the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, giving our body a chance to relax and restore energy reserves. These practices help balance the functioning of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, reducing the effects of stress and improving overall well-being.
In addition, a healthy and balanced diet is important not only for general health, but also for the function of the sympathetic nervous system. Certain foods and nutrients can help support SNS health and reduce inflammation and other stress-related ailments.
Prevention of sympathetic nervous system disorders may include eating a balanced diet, avoiding alcohol and drug use, maintaining a healthy weight and physical activity, using safety equipment when necessary, and managing chronic conditions that can damage the nervous system.
Nutrients that stimulate sympathetic nervous system function
Certain nutrients are especially important for healthy sympathetic nervous system function. The vitamin B complex, including vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9 and B12, is essential for the functioning of the nervous system. These vitamins help nerve cells communicate with each other and are necessary to prevent nerve damage.
-
Sale Product on saleGarden of life Vitamin Code RAW B-COMPLEX – B group vitamins complete with probiotics, antioxidants and enzymes. Bioactive complex, 120 vegan capsules
59,90 €Original price was: 59,90 €.38,90 €Current price is: 38,90 €.
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and nuts also benefit the health of the SNS. They reduce inflammation and help maintain the health of cell membranes, which is important for the efficient transmission of nerve impulses.
-
Sale Product on saleSUPER OMEGA-3 - Norwegian fish oil with Omega-3, 100+30 capsules
67,90 €Original price was: 67,90 €.47,50 €Current price is: 47,50 €.Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings
Magnesium is another important nutrient required for the health of the sympathetic nervous system. It helps regulate nerve and muscle activity, reduces the effects of stress and helps ensure better sleep.
-
Sale Product on saleTrace Minerals Magnis Magnesium 400 mg, 118 ml
29,90 €Original price was: 29,90 €.22,40 €Current price is: 22,40 €.Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 2 customer ratings
Nutrients that impair sympathetic nervous system function
There are also nutrients that can negatively affect the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. Caffeine and alcohol are known stimulants that can over-activate the SNS, causing excessive stress and an increased heart rate.
Too much sugar and processed foods can also have negative effects on the SNS. These foods can cause insulin resistance and increase the inflammatory response, which in turn can cause an imbalance in the sympathetic nervous system.
In addition, trans fats and fatty foods can also have negative effects. They can cause blockages in blood vessels that impede blood flow and can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease associated with SNS hyperactivity.
Symptoms of sympathetic nervous system problems
Symptoms of disorders of the sympathetic nervous system can be varied, but usually include heart rhythm disorders, digestive problems, dizziness or even loss of consciousness when standing up, sweating of the face, sexual dysfunction, etc.
Studies on the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system
The functioning of the sympathetic nervous system can be checked using various tests such as blood tests, blood pressure measurements, electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalogram (EEG), nerve conduction studies, etc.

Medical advances in the treatment of disorders of the sympathetic nervous system
Medical science is constantly improving, and that includes new treatments for disorders of the sympathetic nervous system. For example, new drug therapies designed to reduce the activity of the sympathetic nervous system may help reduce high blood pressure and other cardiovascular symptoms.
Scientific research and advances in technology have allowed doctors to better understand the sympathetic nervous system and develop new treatments. These methods include drugs, surgical interventions, and non-invasive treatments that reduce symptoms and improve patients' quality of life.
One of the innovations is the use of beta-blockers, which reduce the frequency and force of heart contractions, thereby lowering blood pressure. Other drugs, such as alpha blockers, work by relaxing blood vessel walls and also lowering blood pressure. However, the use of drugs must be carefully monitored, as they can cause side effects and interact with other medications.
Surgical interventions, such as sympathectomy, in which part of the sympathetic nervous system is removed or blocked, may be used in severe forms of disorders of this system. Although this can be effective in certain patients, it also carries risks, including potential complications and long-term adverse effects.
In addition, the latest technologies, such as nerve stimulation and biofeedback techniques, allow patients to control the activity of their sympathetic nervous system in a non-invasive way. These techniques encourage patients to develop skills to regulate their body's reactions and reduce symptoms such as stress or anxiety.
Future research directions in the field of the sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system research is an ever-evolving field of science where researchers are searching for new knowledge and technologies that can improve treatment options. One of the most important areas of research is the identification and understanding of genetic factors that affect the functioning of the sympathetic nervous system.
Another important aspect of research is the development of new pharmacological agents that are effective and safer in the treatment of disorders of the sympathetic nervous system. It also aims to improve existing treatment methods in order to reduce side effects and increase the effectiveness of treatment.
In addition, neuroscience and neuromodulation technologies are another promising field of research. These approaches may provide new ways to modulate nervous system activity, alleviating symptoms and possibly restoring normal function in patients with chronic sympathetic nervous system disorders.
Frequently asked questions about the sympathetic nervous system
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system is one of two parts of the autonomic nervous system responsible for preparing the body for the "fight or flight" response by regulating heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate and energy release.
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect our body?
It works through the release of noradrenaline and adrenaline, causing an increase in heart rate, vasoconstriction in certain parts of the body, and mobilization of energy sources such as glucose.
How does the sympathetic nervous system differ from the parasympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system is activated during stress and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, while the parasympathetic nervous system works the other way around, relaxing the body and promoting "rest and digest" states.
Can we control our sympathetic nervous system?
Although direct control of autonomic functions is difficult, certain practices such as breathing exercises and meditation can help reduce sympathetic nervous system activity and promote relaxation.
What diseases or disorders are associated with sympathetic nervous system activity?
When the sympathetic nervous system works out of proportion, it can contribute to a variety of disorders, including high blood pressure, heart disease, panic attacks, and other stress-related conditions.
Conclusions
The sympathetic nervous system is a complex and integral part of our body's functioning that affects many basic functions. Health professionals and scientists are constantly studying the workings of this system in order to expand their knowledge and improve treatment strategies. From new drugs to advanced surgery and non-invasive techniques, medical advances offer hope to those suffering from sympathetic nervous system disorders.
In the future, research advances and the development of new technologies will open up even more opportunities to treat and understand the functioning of this complex system. The efforts and collaborations of the scientific community continue to provide effective and innovative treatments that improve the quality of life of patients around the world.